Hearing is a crucial aspect of a child's development. It plays a vital role in language development, communication, social interaction and learning. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that all newborns should undergo hearing screening before leaving the hospital or within the first month of life. In addition, children should have their hearing checked regularly as they grow older.
What Are the Different Types of Hearing Tests?
A hearing test for a child is often not as simple as a hearing test for an adult. For this reason, hearing care professionals are trained in specific techniques to evaluate the hearing of a child. In addition, there are many different types of hearing tests. Some of them may be used on all ages. Others are used based on your child's age and level of understanding.
- Hearing Tests for Newborns:
- Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE):
The OAE test is a quick and non-invasive hearing screening test that measures the sounds produced by the inner ear in response to a sound stimulus. During the test, a small earphone is placed in the baby's ear, which emits a soft clicking sound. The sounds produced by the inner ear are then recorded by a small microphone in the same earphone. This test is painless and it often takes just a few minutes.
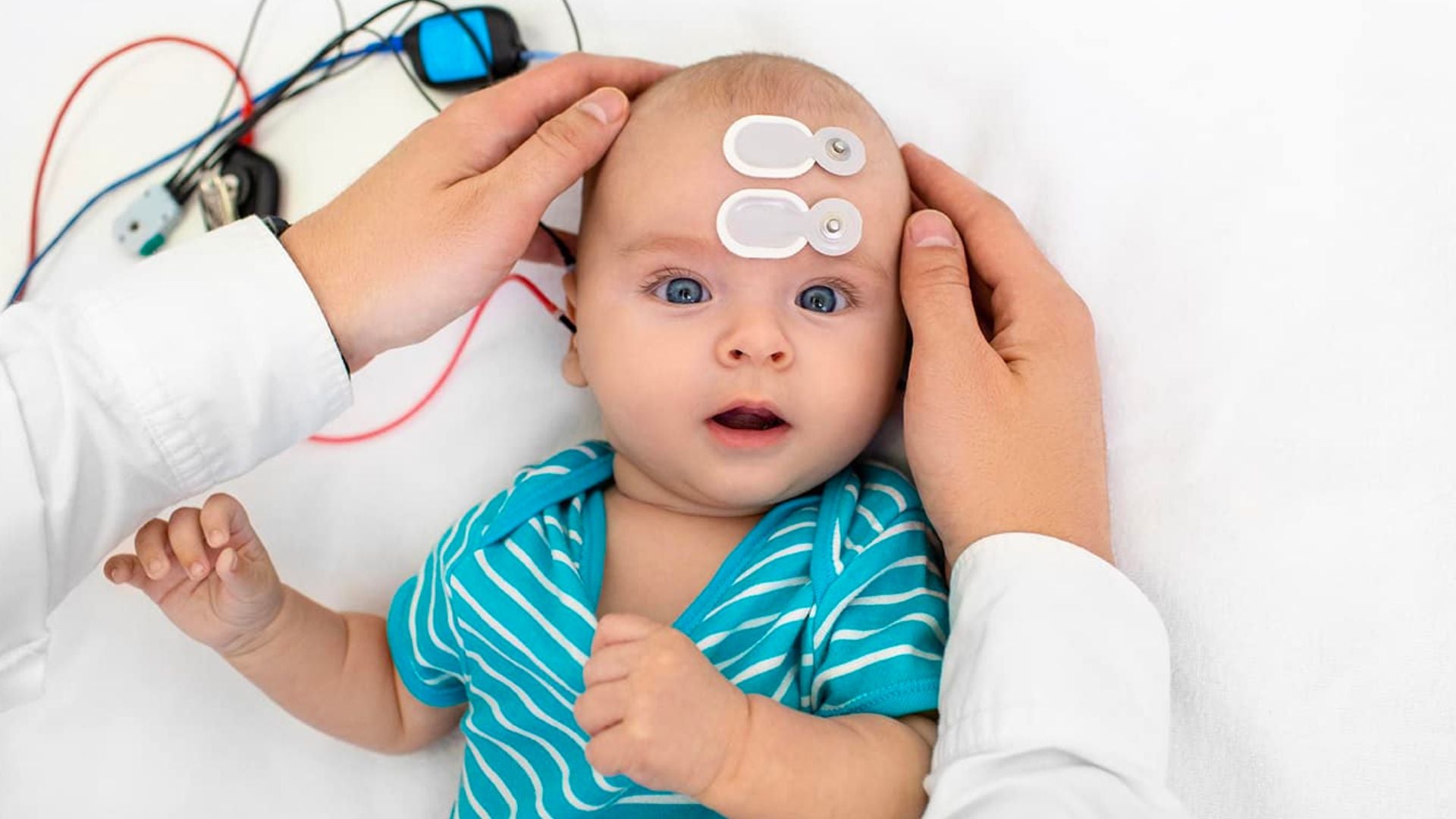
- Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR):
The ABR test measures the electrical activity of the hearing nerve and the brainstem in response to sound. During the test, electrodes are placed on the baby's head to detect the electrical activity. While the baby sleeps, clicking sounds are made through tiny earphones in the baby's ears. Just like in OAE, this test is painless and takes just a few minutes. ABR test is particularly useful for babies who may not be able to respond to sounds during a behavioral test.
There are 2 main types of hearing screening methods for newborns. These may be used alone or together. If the screening tests finds that your child has a hearing loss, more testing is needed. Babies with hearing loss should be identified by age 3 months, so treatment can begin before the baby turns 6 months old to have an optimum outcome for the child's speech and language development.
- Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE):
- Hearing Tests for a Baby
A baby's hearing evaluation may include the OAE and ABR tests above. Also this test may be used: - Behavioral Observation Audiometry (BOA):
The BOA test is a behavioral hearing test that involves observing the baby's response to sounds. The baby is usually placed on their caregiver's lap, and sounds are presented through earphones or speakers. The sounds are varied in intensity and frequency, and the observer records the baby's response, such as head turn or eye movement. This test can be performed on babies as young as a few months old.
- Hearing Tests for a Toddler
A toddler's hearing assessment may include the tests mentioned above, along with these: - Conditioned Play Audiometry (CPA):
A CPA test is a behavioral test that uses an electrical machine to send sounds at different volumes and pitches into your child's ears. During the test, the child is trained to respond to sounds by playing a game, such as placing a toy in a bucket or stacking blocks. The sounds are presented through earphones or speakers, and the child is asked to perform the game when they hear the sound. This test can be used to determine the child's hearing threshold and to assess their ability to hear speech. Since the success of the CPA test relies on the child's cooperation, it is more suitable for children who are older than two years old.
- Visual Reinforcement Audiometry (VRA):
A test where the child is trained to look toward a sound source. When the child gives a correct response, the child is rewarded through a visual reinforcement. This may be a toy that moves or a flashing light. The test is most often used for children between 6 months to 2 years old.
- Hearing Tests for an Older Child:
A hearing evaluation for a child older than age 5 years old may include the tests mentioned above, along with these: - Pure Tone Audiometry:
A test that uses an electrical machine that makes sounds at different volumes and pitches in your child's ears. The child often wears some type of earphones. In this age group, the child is simply asked to respond in some way when the tone is heard in the earphone.
- Tympanometry (also called Impedance Audiometry):
A test that can be done in most healthcare provider's offices to help find out how the middle ear is working. It does not tell if the child is hearing or not. But it helps to find any changes in pressure in the middle ear. This is a hard test to do in younger children because the child needs to sit very still and not be crying, talking, or moving.
When Will My Child's Hearing Be Checked?
Your child's hearing may be checked:
- Within the first month of birth:
This is known as newborn hearing screening and it's often carried out before you leave hospital after giving birth. If you are doing a home birth, you are encouraged to do a hearing screening within one months old.
- From 6 months to 5 years of age:
You may be asked to do another hearing test if you or your doctor has any concerns about your child's hearing as part of your baby's health and development reviews.
It's important for parents to identify their child's hearing problems as early as possible as it can affect your child's speech and language development, social skills and education. With early detection and intervention, most children with hearing loss can learn to adapt and live full, successful lives. To ensure every child is given an equal opportunity to learn and succeed, it's also getting popular for many schools to ask their students to have a hearing test before enrollment.